What is Beta Lactamase Test ?
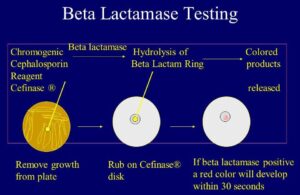
The chromogenic cephalosporinase test is one of the most important tests in clinical laboratories for β – lactamase detection. The substrate is chromogenic cephalosporin, while the test disc is chromogenic cephalosporin. When organisms with β -lactamases are put to the disc, they work by opening the substrate’s β -lactam ring.
Objective of Beta (β) Lactamase Test
To identify the enzyme beta-lactamase, which gives penicillin resistance to a variety of bacterial organisms.
Principle of Beta Lactamase Test
Beta-lactamases are a sort of enzyme generated by a diversity of bacteria and are mediated by genes on plasmids or chromosomes. Antibiotic exposure can either cause or trigger the formation of beta-lactamase. The beta-lactam rings of a variety of susceptible penicillins and cephalosporins are hydrolyzed (and so inactivated) by beta-lactamases. The beta-lactamase enzyme is produced by strains of Staphylococcus aureus, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Branhamella catarrhalis, and Haemophilus influenzae, and the Beta-Lactamase Test detects it quickly. These enzymes provide resistance to a variety of penicillin antibiotics by cleaving the beta-lactam ring of penicillin and cephalosporin antibiotics, causing them to become inactive. Rapid beta-lactamase assays can provide clinically useful information more quickly than MIC or disc diffusion tests. To detect beta-lactamases, several clinical tests have been developed. The iodometric method, the acidometric method, and chromogenic substrates are all examples of these assays. N. gonorrhoeae can be tested using iodometric techniques. With Haemophilus spp., N. gonorrhoeae, and staphylococci, acidometric approaches yield satisfactory findings. To the commercially available beta-lactams, nitrocefin has a wide range of susceptibility and sensitivity. Nitrocef Disks are chromogenic cephalosporins impregnated with nitrocefin. Nitrocefin changes colour from yellow to red when a beta-lactamase hydrolyzes the amide link in a beta-lactam ring. This yellow to crimson colour change on the Nitrocef Disk is caused by bacteria that produce large levels of beta-lactamase. Amoxicillin, ampicillin, penicillin, carbenicillin, mezlocillin, and piperacillin are all penicillinase-labile penicillins that these beta-lactamases can inactivate.
Test Disk
- The Cefinase disc is an example of chromogenic test (BD Microbiology Systems, Cockeysville, Maryland) which is commercially available.
- Nitrocefin is used as the substrate on the disc.
- As the amide link in the beta lactam ring is hydrolyzed by a beta-lactamase, the colour changes from yellow to red fairly quickly.
- The yellow-colored disc in the area where the isolate is smeared turns red when a bacteria produces large levels of this enzyme.
Procedure of Beta Lactamase Test
- Using just a single disc dispenser, pour the disc from the cartridge into an empty petri dish or even on a microscope slide.1 drop of sterile distilled water should be used to moisten the disc.
- Remove a number of well-isolated comparable colonies with a sterilised loop or applicator stick and smear on a disc surface.
- Keep an eye on the disc for any changes in colour.
Polite Follow-Up Email to Professor : When and How You should Write
Result Interpretation of Beta (β) Lactamase Test
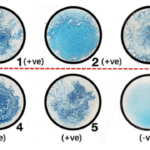
Positive reaction: the colour of the region where the culture is applied changes from yellow to red.
Note that most bacterial strains will produce a positive result within 5 minutes. Positive reactions to some staphylococci, on the other hand, can take up to an hour to appear, and colour changes rarely occur across the entire disc.
Negative reaction: the disc’s colour does not change.
[ninja_tables id=”3900″]Uses of Beta Lactamase Test
Detection of the following is an example of a useful application:
- Penicillin resistance in N. gonorrhoeae
- Ampicillin resistance in H. influenzae
- Penicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus
Limitations of Beta (β) Lactamase Test
- Beta-lactamase detection with the Nitrocef Disk must not completely substitute traditional susceptibility testing methods, since other factors can affect the result of such tests, and innate resistance to beta-lactam antimicrobials has not at all times been linked to beta-lactamase synthesis.
- Avoid over-saturating the tip because this will dilute the reagent.
- It can take up to an hour to detect beta-lactamase activity in staphylococci. Testing growth from the zone margin surrounding an oxacillin disc can help determine whether the enzyme needs to be inducted.
- A negative finding does not rule out the possibility of resistance arising from other mechanisms.
- Because the results may not be predictive of sensitivity to the beta-lactams most commonly employed for therapy, the Nitrocef Disk method cannot be used to screen members of the Enterobacteriaceae, Pseudomonas species, or other aerobic, gram-negative bacilli.
- The Nitrocef Disk cannot be used against organisms that do not produce beta-lactamase, such as Streptococcus pneumoniae and Streptococcus viridans streptococci.
Quality Control of Beta (β) Lactamase Test
Positive for Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 43300).
Positive for Haemophilus influenzae (ATCC 33533)
Negative for Branhamella catarrhalis (ATCC 25240).
Beta Lactamase Test Citations
- https://eportal.mountsinai.ca/Microbiology/manual/tech/tech06.pdf
- https://catalog.hardydiagnostics.com/cp_prod/content/hugo/NitrocefDisks.htm
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11420337/
- https://www.mayomedicallaboratories.com/test-catalog/Clinical+and+Interpretive/8118
- Tille, P. M., & Forbes, B. A. (2014). Bailey & Scott’s diagnostic microbiology (Thirteenth edition.). St. Louis, Missouri: Elsevier.
- Murray P.A., et al. Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 7th ed. 1999.
Related Posts
- Anisocytosis: Definition, Types, Causes, Symptoms, Treatment
- Endospore Staining: Principle, Procedure, Reagents, Results
- Flow Cytometry: Overview, Principle, Steps, Types, Uses
- Northern Blot: Overview, Principle, Procedure and Results
- MPV Blood Test: Calculation, High and Low MPV Value, Results
- Latex Agglutination Test: Objectives, Principle, Procedure, Results
- Iodine Test: Definition, Objective, Principle, Procedure, Results
- Eosin Methylene Blue (EMB) Agar
- Biuret Test for Protein: Purpose, Objectives, Principle, Procedure, Reagents
- Streak Plate Method: Meaning, Principle, Methods, Importance, Limitations
- Bile Solubility Test: Objective, Principle, Procedure, Results, Uses
- Butyrate Disk Test: Objective, Principle, Procedure, Results, Uses, Limitations
- Beta Lactamase Test: Objective, Principle, Procedure, Results, Limitations
- Bacitracin Susceptibility Test: Objective, Principle, Procedure, Results, Uses, Limitations
- Bile Esculin Test: Objective, Principle, Procedure, Result, Uses, Limitations