Bile Solubility Test: Objective, Principle, Procedure, Results, Uses
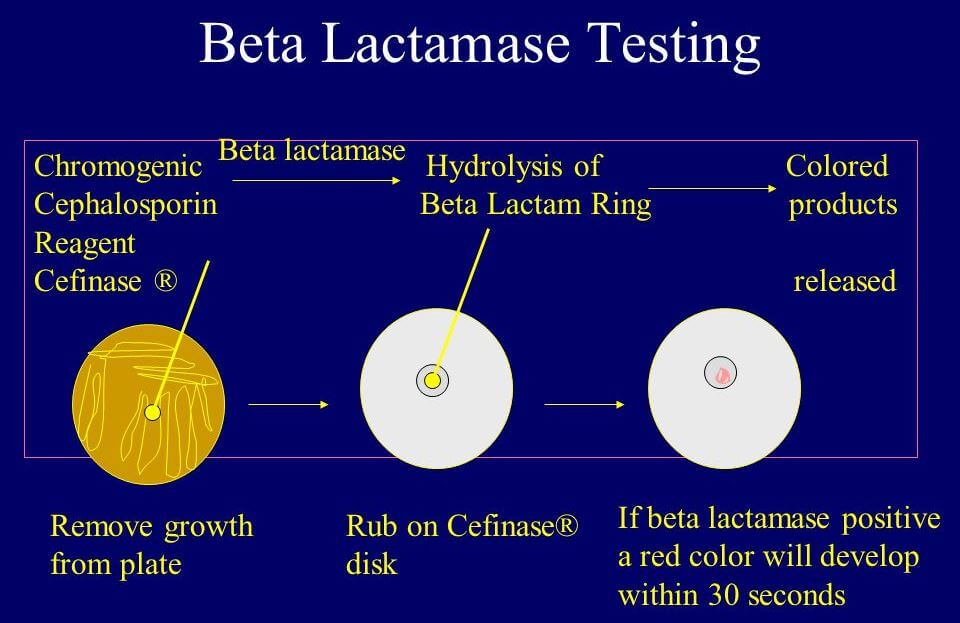
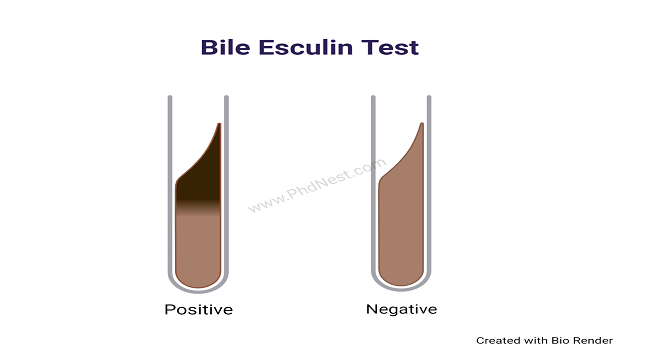
What is Bile Solubility Test ? The bile solubility test is a biochemical test used to distinguish Streptococcus pneumoniae from other alpha-hemolytic Streptococci and to confirm the diagnosis. The bile solubility test has been utilised as a critical test for S. pneumoniae differentiation because it enables for the difficult work of distinguishing between the two … Read more