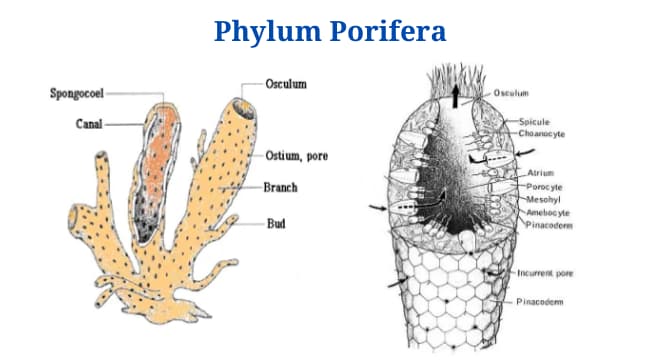
Phylum Porifera: Classification, Characteristics, Examples
Definition of Porifera Porifera are asymmetrical or radially symmetrical multicellular organisms with a cellular grade of organisation lacking well-defined tissues as well as organs; exclusively aquatic; mostly marine, sedentary, solitary or conical animals with a body perforated by pores, canals, as well as cambers through which water flows; with one or more internal cavities lined … Read more