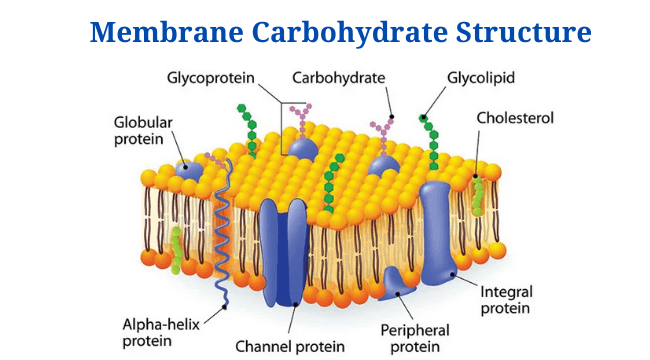
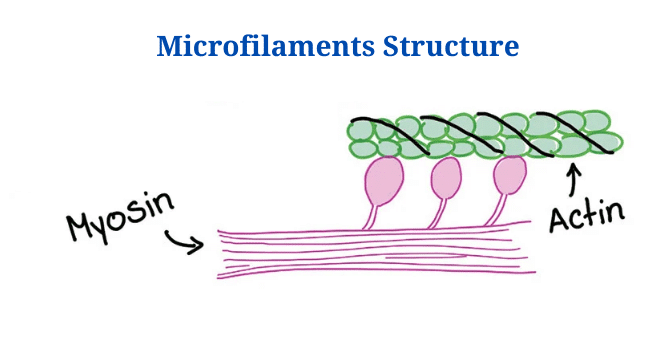
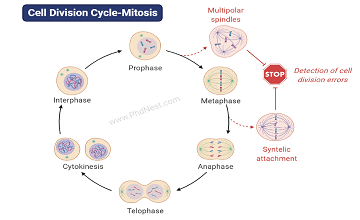
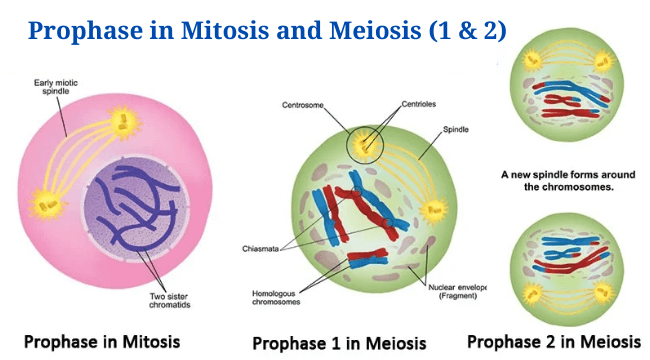
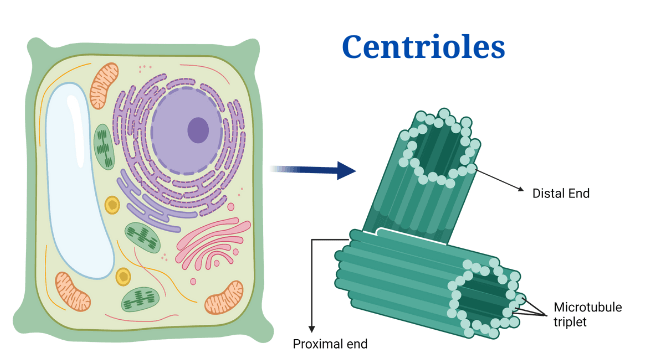
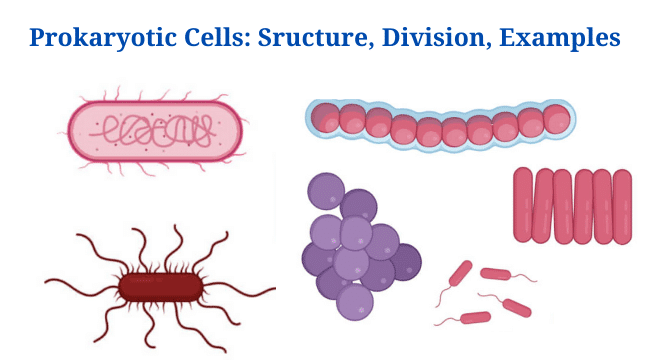
Eukaryotic Cells: Definition, Parts, Structure, Examples
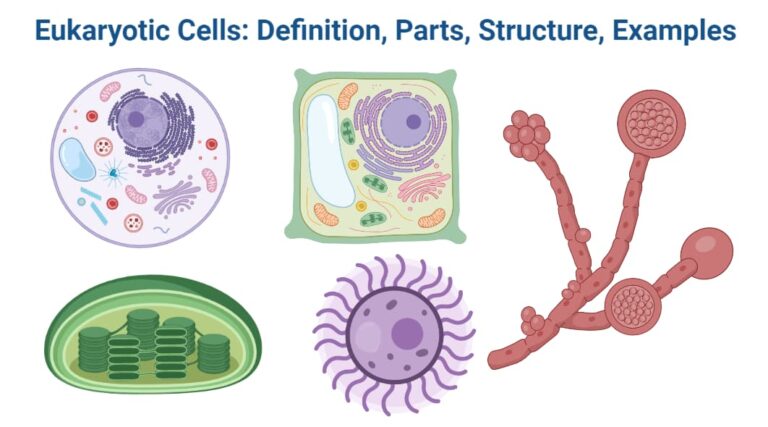
Definition of Eukaryotic Cells Eukaryotic cells feature a membrane-bound, well-defined nucleus as well as several membrane-bound organelles, making them complicated in structure as well as function. The term “eukaryote” comes from the Greek words “eu” as well as “karyon,” which mean “true” as well as “nucleus,” respectively. When compared to prokaryotes, eukaryotic cells have a … Read more