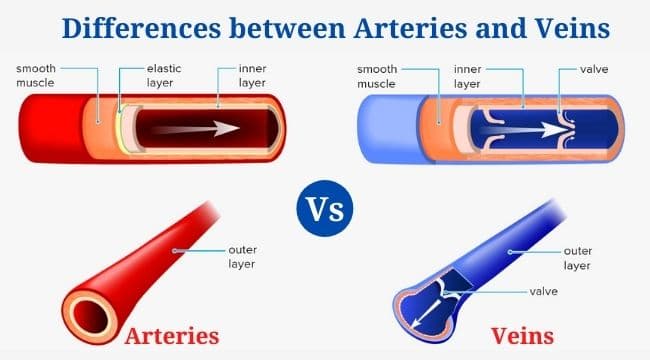
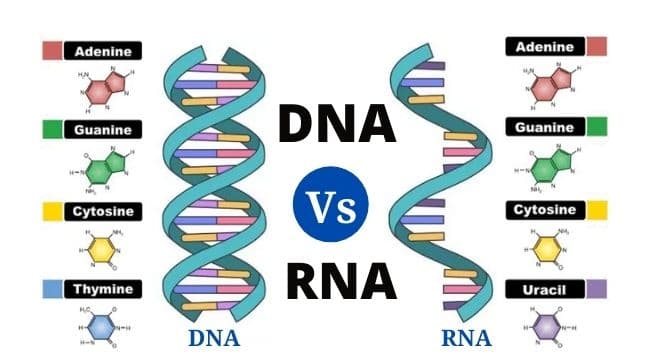
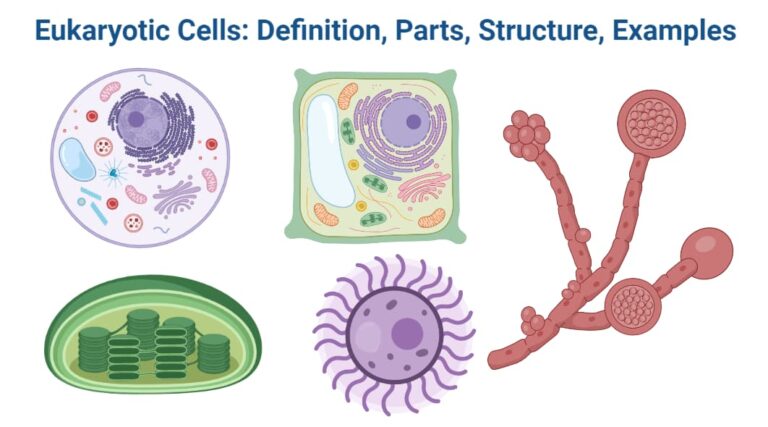
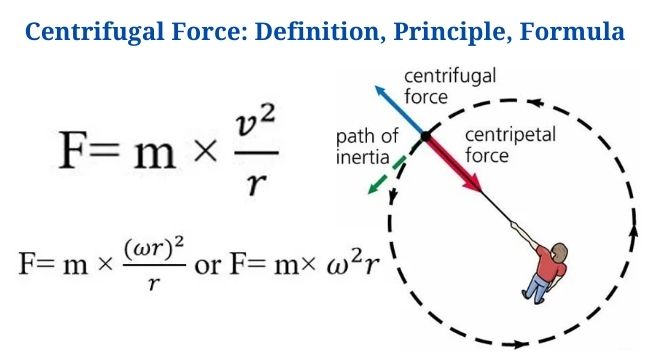
Lineweaver–Burk Plot with Example
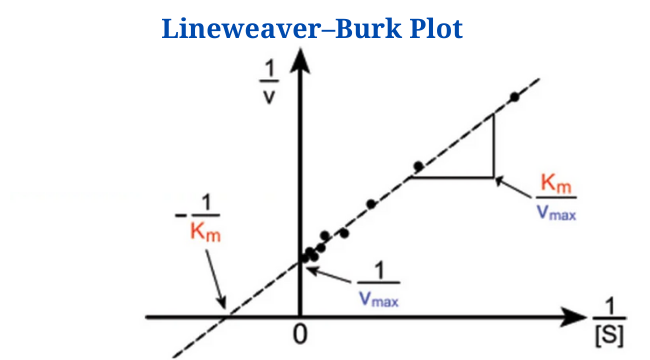
Lineweaver–Burk Plot The Lineweaver–Burk plot (also known as the double reciprocal plot) is a graphical representation of enzyme kinetics used to determine the Michaelis-Menten parameters VmaxVmax (maximum reaction velocity) and KmKm (Michaelis constant). Because Vmax is attained at endless substrate concentration, estimating Vmax and thus Km from a hyperbolic plot is impossible. Due to this issue, Lineweaver and Burk modified the Michaelis–Menten equation … Read more