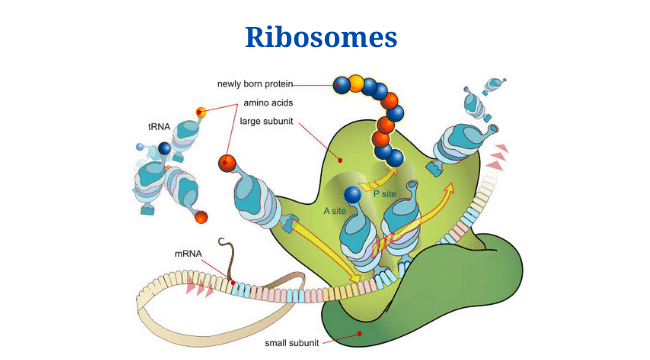
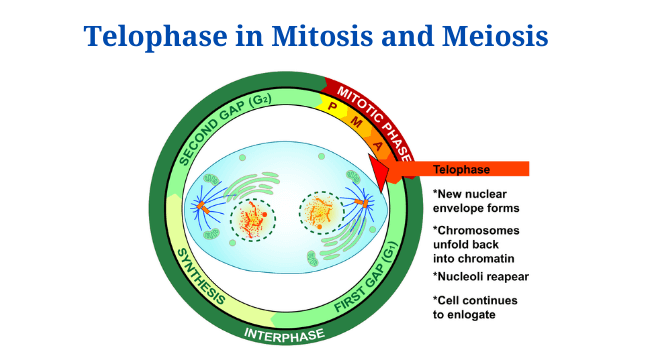
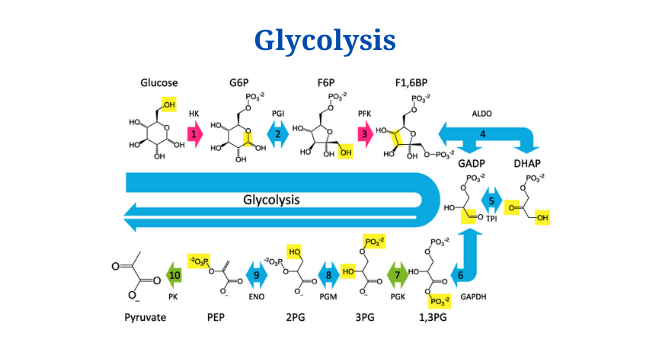
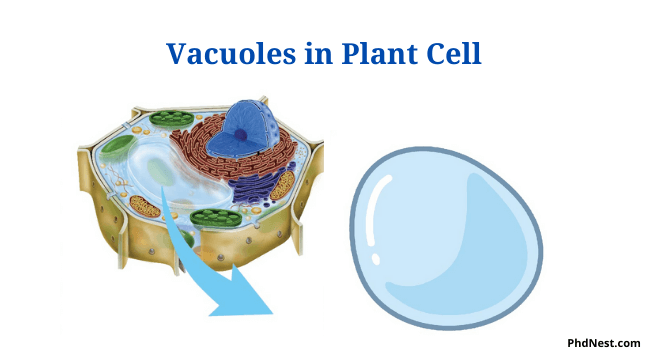
Prokaryotic Cells: Characteristics, Components, Division, Examples
Prokaryotic Cells Definition Prokaryotic cells are single-celled organisms that lack a membrane-bound nucleus and other organelles, making them primitive in form and function. The name “prokaryote” comes from two Greek words: “pro” for “before” and “karyon” for “nucleus.” Prokaryotes, the simplest form of life, are thought to be the first living species on the planet. … Read more