Definition of Anaphase
This is the phase in which the two identical daughter cells are separated from duplicate genetic components carried in the nucleus of the parent cell.
- The sister chromatids (replicated chromosomes) are oriented along the cell’s equator on the metaphase plate in the preceding phase, metaphase.
- As a result, each pair of chromosomes divides into two identical but independent chromosomes during anaphase.
- Mitotic spindles known as microtubules, connected to the chromosomes at both ends of the cell, separate each of these chromosomes.
- At the centromere, chromosomal separation happens simultaneously, and the spindles drag each divided chromosome to the opposing poles of the cell.
- Anaphase’s purpose is to ensure that each daughter cell receives identical sets of chromosomes before the cell cycle’s last phase, telophase.
What happens during Anaphase?
- The anaphase-promoting complex, which ends the metaphase, initiates anaphase.
- This anaphase-promoting complex binds to securin, a protein that aids in the transition from metaphase to anaphase and is also employed to destroy securin by absorbing ubiquitin, thereby functioning as a chaperone inhibitor.
- Securin works by blocking a protease enzyme called separase. When securin is degraded, the separase enzyme is activated, which breaks down the cohesin protein that keeps the sister chromatids together.
- The forces required for the separation of chromatids are created by a number of different microtubules. Astral microtubules, kinetochore microtubules, and interpolar microtubules are among them.
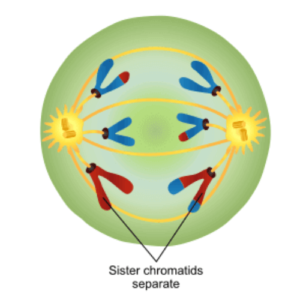
- The centromere splits, causing the sister chromatids to be pulled to the cell poles by the kinetochore microtubules.
- At either pole of the cell, the divided sister chromatids form a V or Y shape.
- The stretching and shaping of the cell, which takes on an oval shape, is aided by astral and interpolar microtubules.
- When chromatids are separated into single sister chromosomes, they contain the same genetic information but operate as separate cells.
- The cell cycle moves on to the following phase, telophase, after anaphase is completed.
What is PhD : Meaning, How to Do, Benefits, Full Details
Anaphase of Mitosis
- The separation of the sister chromatids with the help of separase initiates anaphase in mitosis.
- As the microtubules drag the sister chromatids towards the opposite ends of the cells, Separase destroys the cohesion that keeps them together.
- The astral and interpolar microtubules are responsible for the cell’s oval form by extending and elongating it.
Anaphase of Meiosis
- Meiosis’ anaphase is made up of two successive cell divisions, known as anaphase I and anaphase II.
- Since there is no DNA replication at this stage of meiosis, the diploid cell with two alleles for each gene is reduced to a haploid cell with a single allele for each gene.
- Anaphase I entails separating the chromosomes from each sister chromatid to the opposite poles, which are still linked to the cell’s microtubules, whereas anaphase 2 entails splitting the sister chromatids into single chromatids.
Click Here for Complete Biology Notes
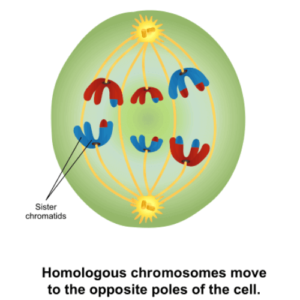
Anaphase I
Figure: Anaphase I in Meiosis. Image Source: Wikipedia
- The kinetochore microtubules shorten during this phase, pulling homologous chromosomes to opposing poles of the cell.
- The centrosomes are pushed apart as the non-kinetochore microtubules lengthen.
- As it prepares to divide at the middle, the cell also lengthens.
- A protein known as Shugoshin (guardian spirit) protects the cohesins surrounding the centromere, preventing sister chromatids from splitting when homologs are segregated.
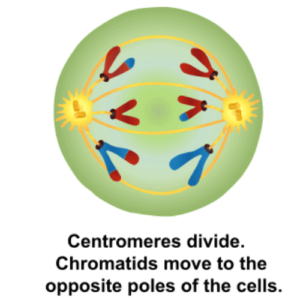
Anaphase II
Figure: Anaphase II in Meiosis. Image Source: Wikipedia
- After metaphase 2, this is the phase in which the remaining centromericcohesins that are no longer protected by the Shugoshin are cleaved.
- This permits the sibling chromatids to be separated and referred to as sister chromosomes individually.
- They travel towards the cells’ opposite poles.
Anaphase of Mitosis and Meiosis Citations
- com/Biology For Major
- https://teaching.ncl.ac.uk/bms/wiki/index.php/Anaphase
- https://www.nature.com/scitable/definition/anaphase-179/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Meiosis#Anaphase_I
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anaphase
- https://www.khanacademy.org/science/biology/cellular-molecular-biology/mitosis/a/phases-of-mitosis
Related Posts
- Phylum Porifera: Classification, Characteristics, Examples
- Dissecting Microscope (Stereo Microscope) Definition, Principle, Uses, Parts
- Epithelial Tissue Vs Connective Tissue: Definition, 16+ Differences, Examples
- 29+ Differences Between Arteries and Veins
- 31+ Differences Between DNA and RNA (DNA vs RNA)
- Eukaryotic Cells: Definition, Parts, Structure, Examples
- Centrifugal Force: Definition, Principle, Formula, Examples
- Asexual Vs Sexual Reproduction: Overview, 18+ Differences, Examples
- Glandular Epithelium: Location, Structure, Functions, Examples
- 25+ Differences between Invertebrates and Vertebrates
- Lineweaver–Burk Plot
- Cilia and Flagella: Definition, Structure, Functions and Diagram
- P-value: Definition, Formula, Table and Calculation
- Nucleosome Model of Chromosome
- Northern Blot: Overview, Principle, Procedure and Results