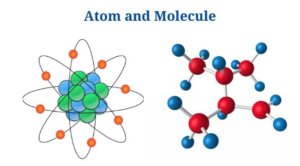
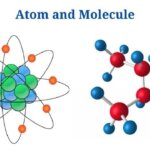
Definition of Atom (What is Atom?)
An atom is the tiniest unit of matter, consisting of a nucleus as well as one or more electrons orbiting it.
- The atom is the basic building block of chemistry as well as is characteristic of each chemical element.
- The atom has a vast empty area in the middle, with a nucleus as well as a cloud of negatively charged electrons filling the rest. The nucleus has a positive charge since it is made up of protons (positively charged)as well as neutrons (neutral).
- When compared to electrons, that are the lightest charged particles in nature, the nucleus is extremely dense.
- The electromagnetic force between the charged species attracts electrons to the protons in the nucleus.
- The atomic number, that specifies the chemical element, is defined by the number of protons in the atom.
- The total mass of the nucleus, that is the total weight of the protons as well as neutrons, determines the atomic weight of an atom.
- The number of neutrons in an atom’s nucleus influences its mass but not its chemical characteristics. Isotopes are nuclei that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons.
- Subatomic particles, such as electrons, neutrons, as well as protons, cannot be separated by chemical reactions.
- Regardless of the number of electrons in the atom, all atoms are roughly the same size. An atom’s radius is around 1-2 Å.
- Different elements’ atoms may or may not exist separately. Atoms of argon as well as helium can exist alone, whereas oxygen, nitrogen, as well as sulphur atoms cannot
- All atoms, with the exception of noble gases, are exceedingly unstable as well as most frequently coexist with other atoms in order to achieve a stable configuration.
Definition of Molecule (What is Molecule?)
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that represents the smallest identifiable unit of a pure material while maintaining the substance’s makeup as well as chemical properties.
- Molecules are produced when atoms are close enough together for their electron clouds to interact with one another as well as with their nuclei.
- When the interaction lowers the overall energy of the system, the atom involved in the interaction forms a chemical bond.
- Based on the number of atoms present in the molecule, monoatomic (single atom)as well as polyatomic (more than one) molecules can be distinguished.
- Molecules might have the same type of atoms (homoatomic) or distinct types of atoms (heteroatomic).
- The number of atoms that remain bonded in a particular type of molecule is fixed.
- Atomic bonds can be ionic or covalent, depending on whether electrons are shared or donated.
- The bonds are frequently directed since the atoms seek to adopt places that enhance bond strengths. The bonds are arranged in such a way that the molecules have a defined, hard structure.
- A molecule’s molecular weight is equal to the sum of the atomic weights of its constituent atoms. In all substances, the number of molecules in a mole is the same, as well as this quantity is known as Avogadro’s number (6.022 ×1023).
- A compound’s molecules can exist independently as well as are frequently far more stable than individual atoms.
- Chemical element symbols, numbers, as well as other special characters such as parentheses, dashes, as well as brackets are used in the molecular formulae of substances.
Key Differences between Atom and Molecule
(Atoms vs Molecules)
[ninja_tables id=”5627″]
Examples of Atom
Atom of oxygen
- Oxygen is a chemical element with eight electrons, protons, as well as neutrons in each atom.
- The oxygen atom is a chemical species that is very reactive as well as unstable. It is frequently formed by chemical reactions.
- Since the oxygen atom’s outermost orbit has six electrons, it tends to link with other oxygen atoms to create a diatomic molecule as well as achieve stability.
- Since oxygen atoms are extremely oxidative, they can induce chemiluminescence in a wide range of analytes.
- Oxygen has an atomic number of 8,that indicates the amount of electrons as well as protons in the atom, as well as an atomic weight of 16. (Mass of the nuclei).
- Oxygen atoms are one of the most numerous atoms in the biosphere, forming various compounds when combined with other atoms.
Examples of Molecule
Molecule of carbon dioxide
- A carbon dioxide molecule is made up of one carbon atom as well as two oxygen atoms linked together by covalent bonds.
- Carbon dioxide is the fourth most prevalent component of air, as well as it is released through respiration by most living creatures.
- A single carbon atom is double-bonded to two distinct oxygen atoms in a carbon dioxide molecule.
- The carbon dioxide molecule is a relatively simple molecular system, but it is significant since it is one of the greenhouse gases that has an impact on life on the planet.
- A CO2 molecule is linear in its electronic ground state, with a C-O bond length of 16Å. Since the electronegativities of the atoms involved differ, the carbon-oxygen bond is polar.
Atoms and Molecules Citations
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. “PubChem Compound Summary for CID 159832, Atomic oxygen” PubChem, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Atomic-oxygen. Accessed 22 February, 2021.
- https://www.britannica.com/science/molecule
- https://www.britannica.com/science/atom/Atomic-mass-and-isotopes
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LvbUrWrMizc
- https://www.toppr.com/guides/chemistry/structure-of-atom/introduction-to-structure-of-atom/
Related Posts
- Dissecting Microscope (Stereo Microscope) Definition, Principle, Uses, Parts
- Saturated vs Unsaturated Hydrocarbons: Definition, Differences, Examples
- Ethanol Vs Methanol: Definition and 10+ Differences
- Hydrogen Bond: Properties, Definition, Types, Examples
- Nitrate Vs Nitrite: Definition, Differences, Examples
- Aromatic Compounds vs Aliphatic Compounds: Definition, Differences, Examples
- Compound Vs Mixture: Definition, Differences, Examples
- Elements Vs Compounds: Definition, Differences, Examples
- Molecules Vs Compounds: Definition, Differences, Examples
- Hard water Vs Soft water: Definition, Differences, Examples
- Glucose Vs Sucrose: Definition and Key Differences
- 13+ Difference Between Atom and Molecule with Examples
- How to Balance Chemical Equation: Methods, Steps, Examples
- Ionic Bond: Definition, Properties, Examples
- Amylase Vs Amylose: Definition, Differences, Example