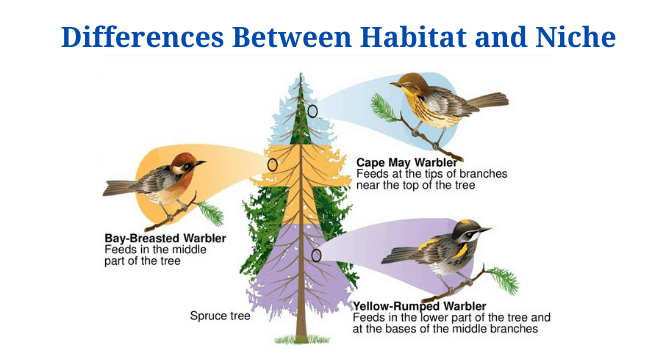
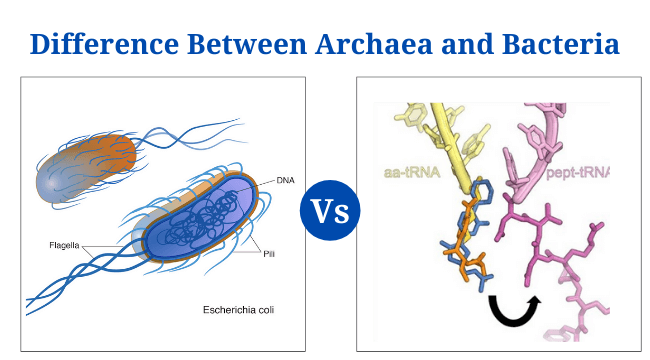
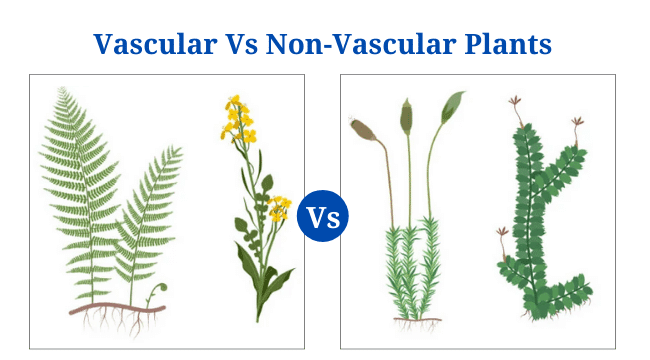
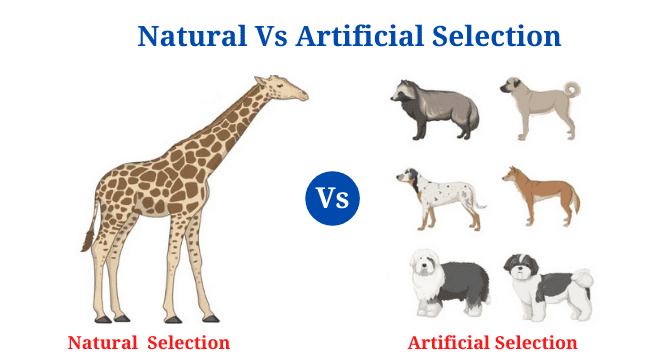
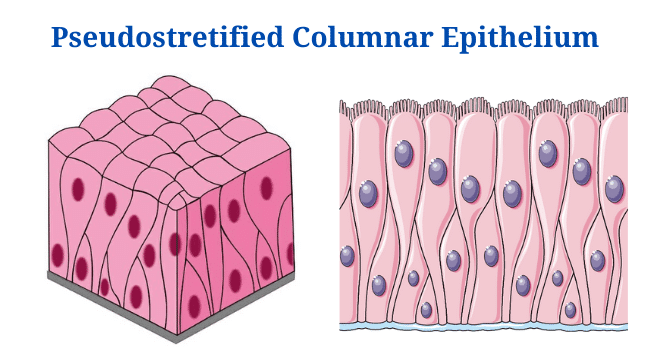
Habitat Vs Niche: Definition, 15+ Differences, Examples
Habitat Definition A habitat is a natural setting in which a certain organism lives and relies on its surroundings for survival, food, shelter, protection, and mating. The word habitat comes from the Latin word ‘habitare,’ which meaning ‘to occupy.’ The physical and biological aspects of an organism’s habitat define it. The nature of the soil, … Read more