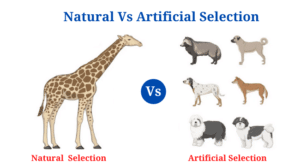
Natural Selection Definition
Natural selection is the process by which an organism adapts to its changing environment by making selective changes to its genotype or genetic makeup.
- Natural selection, along with mutation, genetic drift, and migration, is one of the four fundamental mechanisms of evolution.
- During his evolutionary investigations, Charles Darwin popularised the concept of natural selection.
- Natural selection, according to Darwin, is not a purposeful process that is triggered by changes in the environment and the genotype of organisms.
- Natural selection preserves and passes down changes in an organism’s genotype that boost its chances of surviving and reproducing to the next generation.
- However, as the number of generations grows, the less beneficial alterations are lost.
- Natural selection leads to the formation of new niches, which may lead to speciation. Natural selection is thus an important evolutionary mechanism.
- Natural selection may occur as a result of differences in survival, fertility, mating success, or other life cycle characteristics.
- These alterations, no matter how minor, could result in natural selection over many generations if they are heritable.
- Nature thus ‘selects’ species with specific favourable features that lead to a reproductive advantage, resulting in evolutionary change.
- When considering natural selection, the concept of fitness is critical. An animal’s fitness is determined not just by how long it lives, but also by how well it reproduces.
- As a result, if one animal lives half as long as the others but has twice as many children that live to adulthood, the animal is regarded more fit and will be ‘selected’ by nature.
- Competition, in which the more fit people compete with the less fit for food, housing, and other resources, is another process that ensures natural selection.
- The less fit people die out as a result of this competition, leaving the more fit individuals to survive and reproduce.
- Natural selection, on the other hand, is a long-term process that takes many generations to manifest its consequences.
- It happens in a natural population, resulting in a great amount of biological diversity that may or may not be random.
- Within a species, increased variety leads to an increase in heterozygous genotypes.
- Natural selection can be seen in the selection of long-necked giraffes and the changes in the size and shape of bird beaks based on feeding patterns.
Artificial Selection Definition
Artificial selection, often known as selective breeding, is the act of humans identifying desired qualities in animals and plants and breeding these traits to produce desirable phenotypic traits.
- Although artificial selection uses the same principle as natural selection, artificial selection is a human-controlled process, whereas natural selection is a result of natural forces.
- The artificial selection process is based on Charles Darwin’s research, which determined that selective breeding causes desired changes over time.
- Artificial selection, unlike natural selection, does not lead to evolution or speciation.
- Artificial selection is a much faster process, with results visible within a few generations.
- To develop crossbred plants and animals, desirable phenotypic features in domesticated animals and plants are frequently selected.
- Farmers use this choice in order to increase productivity and improve quality.
- In animals, artificial selection starts with purebred animals with a single breed and desirable traits, which are then bred with other purebred animals to enhance and maintain exceptional qualities.
- Inbreeding, line breeding, and out crossing are all examples of artificial selection in animals.
- Hybrid vigour refers to the greater vigour of hybrids created by selective breeding. However, these breeding practises can sometimes lead to a loss of quality.
- Plant breeding uses a similar approach to domesticate wild plants into uniform and predictable agriculture.
- Plant breeding follows the same process, with plants with desirable qualities such as increased output being bred to maintain and even acquire superior traits.
- Selective plant breeding has been utilised in agriculture for thousands of years; nevertheless, it is now being employed in research on transgenic plants that are homozygous for multiple genes.
- Even while artificial selection is a regulated process, it can happen accidently during farming, resulting in either good or unfavourable results.
- Artificial breeding has several advantages, including increased productivity and healthier offspring, as well as easier and faster offspring analysis.
- Artificial selection, on the other hand, has several drawbacks, such as the fact that it cannot be performed on an entire population at once and that the operations must be carried out in a lab or a greenhouse.
- Artificial selection also reduces genetic diversity in a population by breeding the most fit species together, increasing homozygous genotypes.
- Dog breeding to create new varieties of dogs and cross-breeding in cash crops like wheat and rice are two examples of artificial selection.
Difference Between Natural and Artificial Selection
(Natural Selection Vs Artificial Selection)
| Basis for Comparison | Natural selection | Artificial selection |
| Definition | Natural selection is the process by which an organism adapts to its changing environment by making selective changes to its genotype or genetic makeup | Artificial selection, often known as selective breeding, is the act of humans identifying desired qualities in animals and plants and breeding these traits to produce desirable phenotypic traits. |
| Process | Natural selection is a process that occurs naturally. | Artificial selection is a process that is created artificially or by humans. |
| Occurs in | Natural selection occurs in natural populations under natural circumstances. populations. | Artificial selection takes place in human-created domesticated populations. |
| Chances of survival | As a result of natural selection, a fit organism’s chances of survival improve. | If not done appropriately, an organism’s chance of survival may be jeopardised. |
| Rate | Natural selection is a long-term process that takes many generations to accomplish. | Artificial selection is a speedier procedure that takes days or weeks to complete and has more noticeable results. |
| Controlled by | Natural selection is not as well-controlled as artificial selection since it is governed by natural processes. | Because humans are in charge of artificial selection, it can be better managed. |
| Performed on | Natural selection may occur in all living things on the planet. Artificial selection can be done selectively on specific groups of animals and plants. | Artificial selection can be done selectively on specific groups of animals and plants. |
| Traits |
Natural selection is based on an animal’s adaptive traits.. | Artificial selection is based on human-selected desired characteristics. |
| Natural selection only passes on desirable or favourable qualities to subsequent generations. selection. | Only the selected qualities can be carried down via consecutive generations due to artificial. | |
| Affects | Natural selection has an impact on a species’ entire population. | Artificial selection only has an impact on the persons who are chosen. |
| Diversity | Natural selection is responsible for a great deal of biological variation. | Artificial selection only results in desirable modifications and features, as well as a reduction in genetic variation. |
| Evolution | Speciation and evolution over many generations are aided by natural selection. | Evolution is not aided by artificial selection. |
| Scale | Natural selection has a wide-ranging impact on the natural environment. | Only economically significant individuals are subjected to artificial selection. |
| Hybrid vigor | Natural selection results in hybrid vigour in progeny. | Due to the preservation of desired features, hybrid vigour is lost during artificial selection. |
| Effort | Natural selection is a self-sustaining process that requires no human intervention | Artificial selection could be time-consuming and costly. |
| Genotype | The proportion of heterozygous genotype increases after natural selection. | The proportion of homozygous genotype increases after artificial selection. |
| Examples | Natural selection can be seen in the selection of long-necked giraffes and the changes in the size and shape of bird beaks based on feeding patterns. | Dog breeding to create new varieties of dogs and cross-breeding in cash crops like wheat and rice are two examples of artificial selection. |
Click Here for Complete Biology Notes
Natural Selection Examples
Selection of Long-Necked Giraffes
• A typical example of natural selection is the separation of long-necked giraffes from short-necked giraffes.
• Both long-necked and short-necked giraffes are thought to have existed on Earth many generations ago.
• However, as time passed, the land’s food supply became short. As a result, these giraffes had to eat leaves from the tops of lofty trees.
• These leaves were easily accessible to the long-necked giraffes, but not to the short-necked giraffes. As a result of the scarcity of food, the short-necked giraffes were extinct, while the long-necked giraffes survived.
• The lack of grasses in this example is an environmental shift that makes the selection of more ‘fit’ individuals more difficult.
How to increase Brain Power – Secrets of Brain Unlocked
Sexual Selection in Peacocks
• Many male peacocks compete to locate a suitable mate in peacocks.
• Male peacocks have long bright and attractive tails that attract female peacocks as a result of natural selection.
• Males with brilliant tails are so successful in enticing females, despite the fact that their ability to collect food or breed is unrelated.
• As a result, males with larger tails are naturally preferred over those with smaller tails.
• Other birds, such as ducks and tropical birds, use a similar system where the males are more ornamented than the females.
Artificial Selection Examples
Dog Breeding
• Dog breeding is a widespread occurrence, and it’s thought that purebred dogs have been purposefully selected for at least 14,000 years.
• The goal of ancient breeding was to create a nicer, faster, and more useful version of the existing ancestors.
• These canines were improved in order to improve their hunting prospects and their ability to protect their human owners.
• As humans began to keep dogs as pets, the aim of the dog shifted from guarding the house to shocking invaders, and dogs like the greyhound were interbred to create robust and active breeds.
• Dogs are now commonly maintained at home and serve as companions for the majority of people. As a result, artificial breeding’s goal shifted to producing friendlier and cuter canines like poodles and bulldogs.
Selection of Cash Crops
• Crop selection via artificial means has been used for a long time.
• The Triticum monococcumor einkorn wheat, which was first cultivated in Asia about 40,000 years ago, is thought to be the ancestor of all wheat species found today.
• To improve wheat productivity and species, this plant was inbred or crossbred with various other species.
• Diverse types of wheat are currently used for different reasons, such as wheat used in beer manufacturing versus wheat used in pasta and other noodles.
• These species are created by selecting species that are appropriate for their various uses.
Natural Selection Vs Artificial Selection Citations
- https://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/article/evo_25
- https://www.thoughtco.com/about-artificial-selection-1224495
- https://www.slideshare.net/jacquiepetit/test-questions-artificial-selection-period-4
- https://www.newscientist.com/term/natural-selection/
- https://www.differencebetween.com/difference-between-natural-selection-and-vs-artificial-selection/
- https://www.crystalinks.com/plantbreeding.html
- https://www.britannica.com/science/evolution-scientific-theory/The-science-of-evolution
- https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/topics/zpffr82/articles/z7hj2nb
- https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/guides/zgq96yc/revision/2
- https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/guides/z6trd2p/revision/3
- https://vivadifferences.com/difference-between-natural-and-artificial-selection/
- https://quizlet.com/74934139/bio2-exam-1-flash-cards/
- https://examples.yourdictionary.com/examples-of-natural-selection.html
- https://besjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/1365-2656.12488
Related Posts
- Phylum Porifera: Classification, Characteristics, Examples
- Dissecting Microscope (Stereo Microscope) Definition, Principle, Uses, Parts
- Epithelial Tissue Vs Connective Tissue: Definition, 16+ Differences, Examples
- 29+ Differences Between Arteries and Veins
- 31+ Differences Between DNA and RNA (DNA vs RNA)
- Eukaryotic Cells: Definition, Parts, Structure, Examples
- Centrifugal Force: Definition, Principle, Formula, Examples
- Asexual Vs Sexual Reproduction: Overview, 18+ Differences, Examples
- Glandular Epithelium: Location, Structure, Functions, Examples
- 25+ Differences between Invertebrates and Vertebrates
- Lineweaver–Burk Plot
- Cilia and Flagella: Definition, Structure, Functions and Diagram
- P-value: Definition, Formula, Table and Calculation
- Nucleosome Model of Chromosome
- Northern Blot: Overview, Principle, Procedure and Results