Simple Cuboidal Epithelium Definition
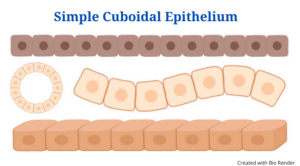
Simple cuboidal epithelium is a form of simple epithelium made up of cube-shaped cells with rounds and a nucleus that is more or less in the centre. They are generally created to better suit the function of specific organs. All of the cube-shaped cells are directly linked to the basement membrane since the simple cuboidal epithelium contains a single layer of cells.
Structure of the Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
- Because the cells of the cuboidal epithelium cannot form ducts, they are not precisely cubical. They are, however, about as tall as they are wide.
- The cells are thicker, with a bigger and more circular nucleus in the centre.
- The cells are comparable in shape and size, being more or less cube-like in shape.
- Because of their higher thickness, cytoplasm can be found in abundance in mitochondria and other organelles, allowing for efficient active transport across the epithelium and other tasks.
- As the epithelium serves as a protective covering or lining, the cells are densely packed, with almost no intracellular space between them.
- The apical surface of the cells of the cuboidal epithelium, like all other forms of epithelial tissues, faces the lumen of the organs or ducts, while the lateral surface is lined with adhesions and junctions to help connect adjacent cells.
- On the apical surface, cells in the simple cuboidal epithelium, such as tissue in the respiratory bronchioles and tubules in the kidneys, are ciliated.
- The cilia are usually 5-10 metres long and 0.2 metres wide. The core structure of each cilium is made up of nine peripheral microtubule doublets surrounded by two central microtubules.
- Cilia have rapid beating patterns that carry a stream of fluid and suspended particles down the epithelium in one direction.
- These cilia help excretion and secretion by directing the passage of chemicals in a specific direction.
- There is no direct blood supply to the cells in the basic cuboidal epithelium. Even so, because they are intimately linked to the basement membrane, they obtain their nutrition, water, and gases from the underlying tissue via diffusion.
- The cells, on the other hand, are innervated and have a nerve supply.
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium Functions
The key functions of the simple cuboidal epithelium are secretion, absorption, and covering due to the shape of the cells.
- Protection/Covering
- They serve as a protective layer for numerous organs, shielding them from injury and other toxins.
- The ovarian surface is formed by the cuboidal epithelium in the ovaries, which replaces and repairs the damage caused by ovulation and supports the function of the ovum in the ovary.
- They also protect the outer lining of the testes’ seminiferous tubules.
- In other regions of the body, such as the lining of the ducts in the respiratory system, the cuboidal epithelium serves as a lining and protects the internal structure. Providing mechanical wear and tear resistance.
- Suppression
- They are also responsible for the production of physiologically active fluids such as cerebrospinal fluid and hormones.
- The cuboidal epithelium of the thyroid glands, which lines the thyroid follicles responsible for thyroid hormone production, is an example of this.
- A single layer of cuboidal cells that create cerebrospinal fluid forms the ependyma in the brain.
What is PhD : Meaning, How to Do, Benefits, Full Details
- Urination
- They also help with excretion, as the kidneys expel toxic by-products into the urine.
- Similarly, the lining of the sweat and sebaceous glands is derived from the simple cuboidal epithelium that produces sweat and oil products.
- The active transport process required for the removal of diverse compounds is aided by a high number of mitochondria and other organelles.
- Assimilation
- The cells of the simple cuboidal epithelium may be involved in active or passive material transport depending on their position.
- The simple cuboidal epithelium lined proximal convoluted tubules and distal convoluted tubules of the kidneys eliminate excess water and other waste items while also maintaining the body’s pH and ion balance.
- The cilia found on the apical surface of the cuboidal epithelial cells in the kidneys that help in absorption.
Location and Examples of Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
- They can be found all over the body, and their function varies according on the organ.
- They provide covering as well as excretory and absorptive functions by lining the respiratory tract, kidney tubules, and smaller ducts of many other glands.
- The thyroid follicle is another example of simple cuboidal epithelium in the thyroid glands.
- They cover the ovary’s surface, the epididymis, and a portion of the testes.
- Similarly, this epithelium can be found on the anterior surface of the capsule of the lens of the eye, as well as on the posterior side of the retina of the eye, where it forms the pigmented epithelium.
- They also make up the secreting parts of several glands, such as the thyroid and pancreas.
Click Here for Complete Biology Notes
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium Citations
- https://quizlet.com/147667159/chapter-4-epithelium-flash-cards/
- https://quizlet.com/157579600/epithelial-tissues-quiz-flash-cards/
- https://www.lecturio.com/magazine/epithelium/
- https://wikimili.com/en/Simple_cuboidal_epithelium
- https://quizlet.com/44569319/ap-i-chapter-4-flash-cards/
- https://jcs.biologists.org/content/117/13/2791
- https://www.toppr.com/guides/biology/tissues/epithelial-tissue/
- https://www.slideshare.net/farhanali911/epithelium-33461392
Related Posts
- Phylum Porifera: Classification, Characteristics, Examples
- Dissecting Microscope (Stereo Microscope) Definition, Principle, Uses, Parts
- Epithelial Tissue Vs Connective Tissue: Definition, 16+ Differences, Examples
- 29+ Differences Between Arteries and Veins
- 31+ Differences Between DNA and RNA (DNA vs RNA)
- Eukaryotic Cells: Definition, Parts, Structure, Examples
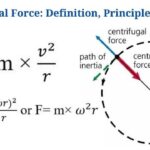
- Centrifugal Force: Definition, Principle, Formula, Examples
- Asexual Vs Sexual Reproduction: Overview, 18+ Differences, Examples
- Glandular Epithelium: Location, Structure, Functions, Examples
- 25+ Differences between Invertebrates and Vertebrates
- Lineweaver–Burk Plot
- Cilia and Flagella: Definition, Structure, Functions and Diagram
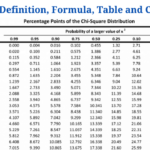
- P-value: Definition, Formula, Table and Calculation
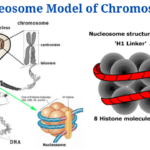
- Nucleosome Model of Chromosome
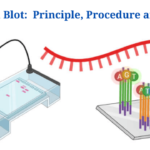
- Northern Blot: Overview, Principle, Procedure and Results