Cell membranes protect and organize cells. All cells have an outer plasma membrane that regulates not only what enters the cell, but also how much of any given substance comes in. Unlike prokaryotes, eukaryotic cells also possess internal membranes that encase their organelles and control the exchange of essential cell components. Both types of membranes have a specialized structure that facilitates their gatekeeping function.
Cell Membrane Definition
- Cell Membrane is a boundary of a cell covered with cell walls.
- The plasma membrane protects the cell from damage caused by environmental exposure.
- Unlike Plasma Membrane, other organelles do not perform such functions.
- The plasma membrane comprises lipids and proteins. It is also known as the cell surface membrane or plasmalemma.
- It encloses every living cell with the help of embedded protein. It has a phospholipid bilayer.
- It helps in the movement of some selective substances to move in or move out
- It is said to be semi-permeable because it works as a barrier between components of cell and environment. It doesn’t allow components to pass out or pass in.
- Functions of Plasma membrane are specific, i.e., transportation, regulations of ions and materials, and Endocytosis.
Click Here for Complete Biology Notes
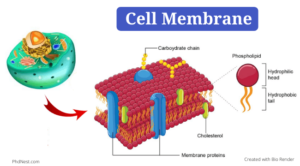
Figure: Diagram of Cell Membrane or Plasma Membrane
Cell Membrane Structure and Composition
The plasma membrane comprises Phospholipids, Cholesterol, Proteins, and Carbohydrates. The proportion of each molecule is different in different cell types. This membrane is not solid but flexible, which helps in floating all the molecules. Mosaic is a term referred to as cell membrane means a substance containing many different parts. So, all these substances are part of the plasma membrane, and the plasma membrane itself is a mosaic.
- The lipids are major components in cell membranes such as lipid bilayers composed of peripheral and embedded proteins.
- The type of lipids in the plasma membrane is phospholipids. It consists of a head group exposed to the aqueous environment and fatty acid tails that face the inner side of the bilayer.
- Glycerol-based lipids are composed of phosphatidylinositol (PI), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), phosphatidylcholine (PC), phosphatidylserine (PS), phosphatidylglycerol (PG), cardiolipin (CL), and phosphatidic acid (PA).
- The sphingomyelin (SM) is a sphingosine-based lipid.
- Cholesterolis present in eukaryotic membranes and maintains membrane fluidity at a variety of temperatures. Fluidity is also found with the help of unsaturated fatty acids’ concentration in the membrane, which is liquids at room temperature, and the chain length of the fatty acids.
- The embedded proteinsin the plasma membrane have various functions such as transporting and channeling compounds, as a receptor for covering hormones and as a structural protein
- The peripheral membrane proteinshelp in the movement of the membrane with the support of the inner membrane skeleton or the cortical skeleton.
- Glycophosphatidylinositol (GPI)glycan-anchored proteins are the third type of protein. The prion protein present in the neuronal membranes is an example of GPI.
- A highly charged membrane is attached, known ad glycocalyx’s Hain of carbohydrates that prevent cells from digestion. It also helps as barrier uptake of hydrophobic molecules.
How to increase Brain Power – Secrets of Brain Unlocked
Note:
- Membrane lipids are a chemical that consists of both hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties. So, they are also considered antipathetic.
- Lipids and proteins can move inside the membrane. The flexibility of the membrane helps them to move freely.
Cell Membrane Functions
The most important membrane in animal cells is the plasma membrane. There are other important membranes, such as the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and the Golgi apparatus.
Plants cells contain different varieties of membrane such as the plastids and vacuoles.
There are the following functions of Membranes and their components.
1 . Enclosed cells:
- Enclosing cells and organelles by cell membrane protect cells from the external environment.
- The plasma membrane helps in balancing the concentration of various substances
2. Balanced Regulation of Substances:
- This helps in maintaining the concentration of substances. It can find the condition of the cell before the process of homeostasis. This is necessary for the cell to have regulated the transport of substances through channels of a cell.
3. The concentration of ions:
- It helps in regulating and balancing ions. Lipid soluble materials can move freely. But charged particles cannot move out of this membrane.
4. Transmission of the nerve impulse: Enzymatic catalysis of reactions.
- Neurons’ cell membrane helps in transmitting nerve impulses.
- It functions as a coordinator of the body
5. Association with other cells
- It functions in interaction with other cells for tissue formation.
6. Monitoring the cytoskeleton
- It helps in maintaining the shape and providing the movement of organelles and cells.
Cell Membrane Citations
- Koolman, J., & Röhm, K.-H. (2005). Color atlas of biochemistry. Stuttgart: Thieme.
- Alberts, B. (2004). Essential cell biology. New York, NY: Garland Science Pub.
- https://www.mheducation.co.uk/he/chapters/9780071102087.pdf
- http://www.nslc.wustl.edu/courses/bio101/cruz/Organelles/Organelle.htm
- https://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/cell-membranes-14052567/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK9928/
Related Posts
- Phylum Porifera: Classification, Characteristics, Examples
- Dissecting Microscope (Stereo Microscope) Definition, Principle, Uses, Parts
- Epithelial Tissue Vs Connective Tissue: Definition, 16+ Differences, Examples
- 29+ Differences Between Arteries and Veins
- 31+ Differences Between DNA and RNA (DNA vs RNA)
- Eukaryotic Cells: Definition, Parts, Structure, Examples
- Centrifugal Force: Definition, Principle, Formula, Examples
- Asexual Vs Sexual Reproduction: Overview, 18+ Differences, Examples
- Glandular Epithelium: Location, Structure, Functions, Examples
- 25+ Differences between Invertebrates and Vertebrates
- Lineweaver–Burk Plot
- Cilia and Flagella: Definition, Structure, Functions and Diagram
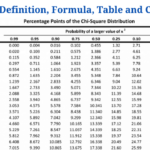
- P-value: Definition, Formula, Table and Calculation
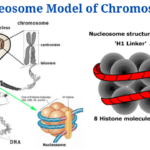
- Nucleosome Model of Chromosome
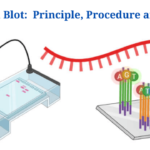
- Northern Blot: Overview, Principle, Procedure and Results