Cockroaches belong to the order Blattodea, the family of Blattidae and the Genus Periplaneta. There are around 4000 different species of cockroach around the world. However, only a few of them can be found in the Indian subcontinent.
Some of the common species include – German cockroach (Blatella Germanica), American cockroach (Periplaneta Americana), oriental cockroach (Blatta Orientalis) and the brown-banded cockroach (Supari Longipalpa). To know more about the different species of cockroach and their scientific names, refer to our morphology and anatomy of cockroach notes.
Cockroach
- Brown/black body, bright yellow, red & green in tropical.
- Size 1/4th inch to 3 inches (0.6 -7.6 cm), long antennae, legs, the flat extension of upper body conceals Head, serious pests, reside in human homes.
- Nocturnal omnivores, damp place throughout the world.
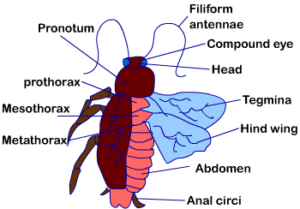
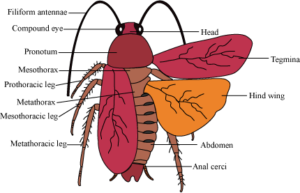
Morphology of Cockroach
- Segmented, divisible to head, thorax, abdomen.
- The chitinous exoskeleton, hardened plates – Sclerites (tergite dorsally & sternite ventrally), joined by thin & flexible articular membrane.
- Adults – Peri planta Americana (34 – 53 mm), wings extended beyond the tip of the abdomen in males.
- Head – triangular, anteriorly at 900 to the body axis, a fusion of 6 segments, mobility in all direction (flexible neck), bears compound eye. Thread is antennae from sockets in front of the eye.
- Antennae – Sensory receptor, monitor Environment.
- Anterior mouth – Biting & chewing.
- Mouth – Labrum (upper lips, pair of mandibles, pair of maxillae, labium (lower lip)
- Median flexible lobe acting as the tongue (Hypopharynx) within the cavity by mouth.
- Thorax – Prothorax, mesothorax, metathorax.
- The Head is connected to the thorax by the neck (short extension of prothorax). Each thoracic segment – pair of legs.
- First pair of wings – mesothorax, Second pair – metathorax
- Forewings (mesothoraces) – tegmina are dark, opaque, bather, cover hind wings at rest.
- Hind wings – Transparent, membranous, flight.
- Abdomen in male and female – 10 segments (jointed filamentous structure- anal cerci)
- In female – 7th sternum (boot shape) and with 8th & 9th form brood/genital pouch where anterior has gonopore, spermathecal pore, collateral glands.
- In a male, genital pouch (hind end of the abdomen) dorsally by 9th & 10th terga, ventrally by 9th sternum, has a dorsal anus, ventral genital pore & gonapophysis, bear short, thread-like anal styles (-in females)
Anatomy of Cockroach
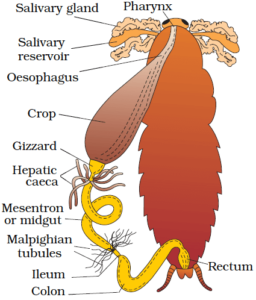
1 .Digestive System of Cockroach
- Foregut + midgut + hindgut
- The mouth opens to the tubular pharynx to the esophagus (tubular passage), opens to sac-like structure – crop (store food), followed by gizzard/ proventriculus.
- Outer thick circular muscle, inner cuticles are forming six chitinous plate – teeth.
- Gizzard in grinding food. The foregut is lined by the cuticle. 6-8 blind tubules – hepatic/gastric Calca at the junction of fore & midgut, secrete digestive juice.
- At the junction of mid & hindgut – ring of 100-150 yellow color thin filamentous Malpighian tubules (remove products from hemolymph)
- Hind gut is broader (ileum + colon + rectum) than mid-gut.
- The rectum opens through the anus.
Click Here for Complete Biology Notes
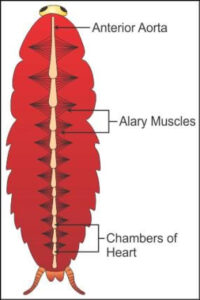
2. Vascular system of Cockroach
- Open types, poorly developed vessels, open to hemocoel.
- Visceral organs in the hemocoel are bathed in the hemolymph.
- Hemolymph – colorless plasma + hemocytes.
- Heart – Elongated tube along the mid-dorsal line of thorax & abdomen, differentiated to a funnel-shaped chamber with Ostia on either side. Blood from the sinus enters through Ostia, pumped anteriorly to sinuses again.
3. Respiratory System of Cockroach
- Network of the trachea, open through 10 pairs of small holes – Spiracles (lateral side), opening by sphincters.
- Branching tubes (tactual tubes -tracheoles) carry O2 from air to all parts.
- Exchange of gases at tracheoles by diffusion.
4. Excretion system of Cockroach
- Malpighian tubules (glandular & ciliated cell)
- Absorbs nitrogenous waste – uric acid – excreted by hindgut.
- Uricotelic, fat body, nephrocyte, reverse glands also help in excretion.
5. Nervous system of Cockroach
- Fused, segmentally arranged ganglia, joined by C.T. on ventral.
- Three ganglia in the thorax, 6 in the abdomen; spread throughout.
- Head holds bit nervous system, rest along the ventral side.
- If the Head is cut off, it will live for one week.
- Brain by supraesophageal ganglion (nerve to antennae & compound eyes).
- Sense organs – antennae, eyes, maxillary palps, labial palps, anal cerci.
- Compound eye – Dorsal side, 2000 hexagonal ommatidia (receive several images) – mosaic vision (increase sensitivity decrease resolution), common at night (nocturnal).
6. Reproductive system of Cockroach
- Dioecious, well developed.
- Male – pair of testes on the lateral side of 4th – 6th abdominal segment, from them vas deferens arise opening to ejaculatory duct through seminal vesicle, then to male gonopore on the ventral side to the anus.
- Mushroom shape gland (6th – 7th) – accessory gland.
- External genitalia – Male gonapophysis/phylloxera (chitinous asymmetrical structure).
- Sperms in the seminal vesicle, glued to form spermatophore.
- Female – Two large ovaries, laterally in 2nd -6th segment.
- Each ovary – group of 8 ovarian tubule(ovarioles) containing chain of developing ova.
- Oviducts unite to a single median oviduct, opens to the genital chamber. Pair of spermatheca (6th) opens to the genital chamber. Fertilized eggs are enclosed in capsule – Oothecal (Dark reddish to blackish capsule),3/8 inch (8mm) long.
- Dropped to suitable surface (crack of high humidity near food sources).
- Female produce 9-10 oothecal (14-16 eggs), pest spoil food (smelly excreta), diseases.
- Many are wild, no economic importance, thrive in or around human habitat.
- P. americana – paurometabolous (div. by nymphal stage), nymph looks like adult, grows by molting about 13 times to reach adult form.
- Next to last nymphal stage has wing pads; only adults have wings.
Related Posts
- Phylum Porifera: Classification, Characteristics, Examples
- Dissecting Microscope (Stereo Microscope) Definition, Principle, Uses, Parts
- Epithelial Tissue Vs Connective Tissue: Definition, 16+ Differences, Examples
- 29+ Differences Between Arteries and Veins
- 31+ Differences Between DNA and RNA (DNA vs RNA)
- Eukaryotic Cells: Definition, Parts, Structure, Examples
- Centrifugal Force: Definition, Principle, Formula, Examples
- Asexual Vs Sexual Reproduction: Overview, 18+ Differences, Examples
- Glandular Epithelium: Location, Structure, Functions, Examples
- 25+ Differences between Invertebrates and Vertebrates
- Lineweaver–Burk Plot
- Cilia and Flagella: Definition, Structure, Functions and Diagram
- P-value: Definition, Formula, Table and Calculation
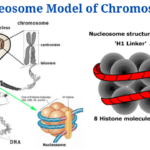
- Nucleosome Model of Chromosome
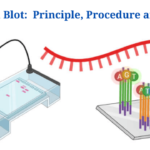
- Northern Blot: Overview, Principle, Procedure and Results