Definition of Cytokinesis
Cytokinesis is a type of physical cellular division which happens following mitosis. Cytokinesis is the actual splitting of the cell cytoplasm, cell membrane, as well as cell organelles to form two different cells when the cell cycle has come to a close in mitosis as well as meiosis.
- Cytokinesis begins in the majority of cells at the anaphase stage and finishes in telophase, when the chromosomes are entirely separated.
- Within animal cells, cytokinesis occurs whenever a contractile ring of microtubules generates a cleavage furrow which separates the cell membrane in half. Microtubules which are utilised in cytokinesis are the ones that are formed throughout the early phases of cell division and help the cell reorganise.
- A cell plate forms in the plant cell, dividing the cell into two halves.
- Furthermore, cytokinesis happens only after full chromosome separation. Every daughter cell acquires chromosomes in their entirety together with all cytoplasmic plus organelle components as a result of this.
What happens during Cytokinesis ?
- Plant and animal cells have identical cytokinesis mechanisms, but the technique by which two daughter cells are formed from a parent cell, including one with a set of divided chromosomes and halved cytoplasm and cell organelles, differs.
- The creation of a cleavage furrow, which splits the cells fairly evenly, is a common part of the cell division process.
- Once a cell takes up the bulk of the cytoplasm, this is known as asymmetrical cell division.
- For example, spermatogenesis is a symmetrical cytokinesis procedure in which newly generated sperm cells are the same in dimension as well as substance, whereas biogenesis is an asymmetrical cytokinesis process that produces a big cell with three polar bodies.
- In animal cells, the position of the mitotic spindles determines the cleavage furrow, whereas The cleavage furrow in plant cells is free from the mitotic spindles.Image
In general, cytokinesis occurs in four stages:
The cleavage furrow’s initiation and creation
- The formation of the cleavage furrow on top of the cell membrane is the first physical change noticed during cytokinesis.
- The furrow deepens and spreads around the cell, eventually dividing it in half.
Constriction and contraction
- Abscission is another term for this.
- The contractile ring, which is composed of actin, myosin, and regulatory proteins generated during cell division, beneath the surface of an animal cell, is responsible for cytokinesis in animal cells.
- These rings have the power to pinch the cell in half by contracting and constricting it.
Membrane Insertion
- During the fusing of intracellular vesicles, a fresh membrane is generated as well as implanted inside the cell membrane close to the contractile ring.
- The new membrane allows the cell to expand while cytoplasmic division occurs.
- Cytokinesis is completed when two completely mature daughter cells are formed.
Completion of cytokinesis by forming two fully developed daughter cells
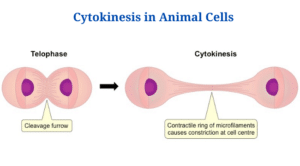
Cytokinesis in animal cells
Figure: Cytokinesis in animal cells. Image Source: BioNinja.
- The contractile ring is thought to play a role in the cytokinesis process in animal cells. The mitotic spindles’ microtubules hold the contractile ring jointly.
- With defining the positioning of the contractile ring, these microtubules as well as cell signals decide the plane of cell division, also referred as the division plane. The cleavage furrow develops all in the region of division plane, squeezing the cell apart and separating it in half.
- The muscle is subsequently contracted and restricted by the contractile ring, that is composed of actin, myosin, and regulatory proteins.
- Actin and myosin are generated and arranged in a cortical network of filaments packed in the midst of actin and myosin throughout interphase.
- Actin filaments restructure as cell division progresses, while myosin filaments collect during anaphase to create contractile rings.
- The actin-myosin as well as regulatory proteins orient the contractile ring and also function as motor proteins, allowing muscle cells to contract.
- Myosin proteins pull actin filaments together to make an actin-myosin ring that is important for the exclusion of cytoplasm and cell organelles.
- Whenever the cytoplasm as well as organelles are eliminated, the ring and microtubules remained behind, making the midbody structure, that ultimately splits.
- The plasma membrane is slashed, preventing fusion, whereas the extracellular components which bind the cell together disintegrate, causing the cells to separate.
- At gap junctions, that are generated by endoplasmic reticulum remains captured by midbody structures, the separated cells might remain linked mostly by cytoplasm.
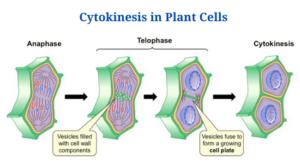
Cytokinesis in plant cells
Figure: Cytokinesis in plant cells. Image Source: BioNinja.
- The central distinction among a plant cell as well as an animal cell is that plants contain an extra-rigid cell wall, that necessitates the use of a unique type of microtubule in the cytokinesis process. The phragmoplasts are what they’re called.
- Vesicular spindle microtubules produced by Golgi vesicles transfer vesicles and cellular components like cellulose towards the new cell wall throughout telophase on the metaphase plate.
- The cell plate, the site of plant cytokinesis, is established at the time the Golgi vesicles merge in the middle, adjacent to the cell wall.
- The phragmoplasts are responsible for transporting cell wall vesicles to the recently created cell plate.
- Throughout interphase, the Golgi apparatus gathers enzymes, structural proteins, as well as glucose molecules in between membranes, that aid in the creation of the fresh cell wall, whereas the Golgi membranes get integrated into the plasma membrane and then become part of it.
- The cellulose carried by the phragmoplast joins as well as mixes to create the plant cell wall’s compound and inflexible matrix.
- The plasma membrane separates the two freshly generated daughter cells after the cell plate separates the cell.
- Plasmodesmata, or gap, between two cells is created by trapped endoplasmic reticulum, permitting chemicals to flow among them and signalling across cells for intercellular communication.
Cytokinesis applications.
- The development of a block-cytokinesis micronuclei cytosome assay to analyse human cells was made possible by cytokinesis research.
- Failed cytokinesis can result in carcinogenesis, that has aided cancer research in terms of oncogenesis as well as therapeutic targets for unmet cytokinesis processes.
Cytokinesis Citations
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2789570/
- https://quizlet.com/200759728/bio-121-chapter-12-flash-cards/
- https://courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-biology/chapter/the-cell-cycle/
- https://www.thoughtco.com/daughter-cells-defined-4024745
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/neuroscience/cytokinesis
- https://www.majordifferences.com/2013/10/difference-plant-cell-vs-and-animal-cell.html
- https://www.genome.gov/genetics-glossary/Plasma-Membrane
- https://www.cell.com/current-biology/pdf/S0960-9822(11)01205-X.pdf
- https://www.annualreviews.org/doi/abs/10.1146/annurev.cellbio.17.1.351
- https://study.com/academy/lesson/actin-filaments-function-structure-quiz.html
- https://quizlet.com/11000697/molecular-biology-of-the-cell-chapter-17-part-3-flash-cards/
Related Posts
- Phylum Porifera: Classification, Characteristics, Examples
- Dissecting Microscope (Stereo Microscope) Definition, Principle, Uses, Parts
- Epithelial Tissue Vs Connective Tissue: Definition, 16+ Differences, Examples
- 29+ Differences Between Arteries and Veins
- 31+ Differences Between DNA and RNA (DNA vs RNA)
- Eukaryotic Cells: Definition, Parts, Structure, Examples
- Centrifugal Force: Definition, Principle, Formula, Examples
- Asexual Vs Sexual Reproduction: Overview, 18+ Differences, Examples
- Glandular Epithelium: Location, Structure, Functions, Examples
- 25+ Differences between Invertebrates and Vertebrates
- Lineweaver–Burk Plot
- Cilia and Flagella: Definition, Structure, Functions and Diagram
- P-value: Definition, Formula, Table and Calculation
- Nucleosome Model of Chromosome
- Northern Blot: Overview, Principle, Procedure and Results