Definition of Oxidation (What is Oxidation?)
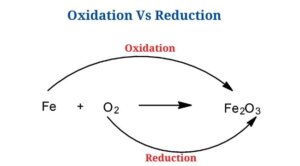
Oxidation is a chemical reaction in which a molecule, atom, or ion loses electrons, increasing the oxidation state of the chemical species.
- Since oxygen gas was the first recognized oxidising agent, the classical concept of oxidation was predicated on the addition of oxygen to a chemical.
- This term corresponds to the concept of electron loss as well as oxidation state rise; however, it was later expanded to cover various types of chemical processes.
- Although the creation of oxides from oxygen molecules is commonly connected with oxidation reactions, it has been discovered that oxygen is not required in such reactions since other molecules can perform the same job.
- Since the loss of electrons from one chemical species results in the gain of electrons in another, oxidation processes invariably occur with reduction events. Redox reactions are the name given to such reactions.
- When a chemical species experiences an oxidation process, it is said to be oxidisedsince its oxidation state increases.
- Oxidizing agents or oxidants are chemical compounds that oxidise other substances. While reducing themselves, oxidants extract electrons from other species.
- Oxidizing agents are also known as electron acceptors since they accept electrons.
Definition of Reduction (What is Reduction?)
Reduction is a chemical reaction in that a molecule, atom, or ion gains electrons, lowering the oxidation state of the chemical species.
- Historically, reduction was defined as the removal of an oxygen atom from a molecule, similar to oxidation.
- Since then, the definition has been updated to cover reactions that cause the chemical species’ oxidation state to decrease.
- In addition, the addition of hydrogen atoms causes the species’ negative charge to rise, resulting in reduction.
- In redox reactions, reduction happens in tandem with oxidation since the loss of electrons during oxidation results in a gain of electrons to other species, resulting in reduction.
- Reducing agents or reductants are chemical compounds that reduce other species. While being oxidised, reducants contribute electrons to other chemical species.
- A chemical species undergoing a reduction process is considered to be reduced when its oxidation state decreases.
- Reducing agents are also known as electron donors since they donate electrons.
Key Difference between Oxidation and Reduction
(Oxidation Vs Reduction)
[ninja_tables id=”5593″]
Oxidation Examples
Respiration of Cells
- In the presence of oxygen, glucose is oxidised into carbon dioxide as well as water through cellular respiration.
- Oxygen is reduced to water since all oxidation reactions also entail a reduction reaction.
- The process’s oxidising agent is the oxygen molecule, which is then reduced.
- As a result of the oxidation process, the oxidation state of carbon atoms changes from 0 to 4, whereas the oxidation state of oxygen changes from 0 to -2.
- Since oxygen is the oxidising agent, cellular respiration comes under the traditional definition of oxidation.
Reduction Examples
Photosynthesis
- In the presence of sunshine, photosynthesis is the conversion of carbon dioxide into a carbohydrate molecule.
- During the process, the carbon dioxide molecule gains electrons, making it less positive as well as more negative.
- As a result of the additional electrons created by photon energy, the total charge of the molecule is lowered.
Oxidation and Reduction Citations
- https://www.thoughtco.com/definition-of-oxidation-in-chemistry-605456
- https://chem301r6.athabascau.ca/unit02.htm
- https://www.britannica.com/science/oxidation
- https://quizlet.com/289641912/chem-redox-reactions-dynamic-module-flash-cards/
Related Posts
- Dissecting Microscope (Stereo Microscope) Definition, Principle, Uses, Parts
- Saturated vs Unsaturated Hydrocarbons: Definition, Differences, Examples
- Ethanol Vs Methanol: Definition and 10+ Differences
- Hydrogen Bond: Properties, Definition, Types, Examples
- Nitrate Vs Nitrite: Definition, Differences, Examples
- Aromatic Compounds vs Aliphatic Compounds: Definition, Differences, Examples
- Compound Vs Mixture: Definition, Differences, Examples
- Elements Vs Compounds: Definition, Differences, Examples
- Molecules Vs Compounds: Definition, Differences, Examples
- Hard water Vs Soft water: Definition, Differences, Examples
- Glucose Vs Sucrose: Definition and Key Differences
- 13+ Difference Between Atom and Molecule with Examples
- How to Balance Chemical Equation: Methods, Steps, Examples
- Ionic Bond: Definition, Properties, Examples
- Amylase Vs Amylose: Definition, Differences, Example