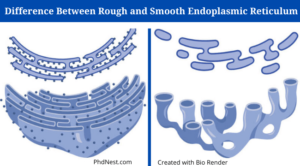
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
The rough endoplasmic reticulum is a form of endoplasmic reticulum that consists of flattened sacs studded on the outer surface with protein-synthesizing particles known as ribosomes.
- The rough endoplasmic reticulum is a component of the cell’s endomembrane system, which is found in the cytoplasm.
- Protein synthesis, folding, modification, and transport to other organelles within and beyond the cell are all handled by the organelle.
- The moniker ‘rough’ ER comes from the fact that ribosomes appear as studs on the surface of the ER under the microscope.
- The RER membrane connects the nuclear membrane to the RER membrane in both plant and animal cells.
- The protein generated in the ribosomes on RER is packaged into vesicles and transferred to the Golgi body, where it is frequently found near the Golgi apparatus.
- The cisternae, which are flattened sacs with sparse tubules, make up the rough ER.
- The membrane also contains an important protein complex called translocon, which is required for RER translation. Ribosomes are connected to the endoplasmic reticulum by a group of proteins known as ribophorins.
- The presence of cytoskeletal components like as microtubules determines the structure of rough ER, and changes in microtubules cause changes in RER structure.
- Furthermore, ribosomes on the rough ER frequently detach and grow into separate cisternae.
- Newly generated proteins undergo minor changes in the RER lumen, such as signal sequence cleavage and glycosylation. Within the lumen, some proteins may change their three-dimensional conformation.
- Rough ER is linked to the formation of lysosomes.
- Rough ER also plays an important function in quality control during protein folding, where the ratio of sheets to tubules changes as the amount of unfolded proteins in the cell grows.
- Apoptosis can be triggered in a cell as a result of an increase in the number of unfolded proteins.
- Similarly, the rough ER contains a number of enzymes involved in RNA metabolism, which bind and alter RNA.
- Protein misfolding in RER, on the other hand, could cause a variety of illnesses. The buildup of misfolded collagen proteins in the RER causes diseases like spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER)
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) is a form of endoplasmic reticulum that is involved in the synthesis and storage of lipids and is made up of tubular vesicles that lack ribosomes on the outer surface.
- The endomembrane system creates key structural lipids like cholesterol and phospholipids, and the smooth ER is a portion of it.
- The absence of ribosomes on the outer surface results in a smooth outer surface, as indicated by the phrase “smooth.” After the shedding of the surface’s ribosomes, smooth ER is created from rough ER.
- Smooth ER is found in both animals and plants, just like rough ER.
- Smooth ER is abundant in the cells of the liver that manufacture steroid hormones in humans.
- Tubules make up the majority of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum. It is usually found close to the cell membrane.
- Spherosomes and oleosomes are frequently connected with these structures.
- Smooth ER has a tubular structure that is visible in human muscle and nerve cells that create networks with other cells.
- Smooth ER create the sarcoplasmic reticulum in muscle cells, which is critical for calcium ion buildup.
- Smooth ER has a dynamic structure that allows new tubules to emerge from the sides.
- These tubules also interact with the cell’s cytoskeletal framework.
- The amount of smooth ER in a cell is determined by the cell’s type, location, and function.
- The smooth ER is also involved for the synthesis of steroid hormones from cholesterol in the endocrine system.
- It produces enzymes in the liver that catalyse processes that remove medicines, metabolic wastes, and toxic chemical compounds. During detoxification, SER’s dynamic structure allows it to gather huge amounts of toxic substances.
- As a result, SER is required for chemical purification and waste disposal.
- Furthermore, the smooth ER contains the glucose-6-phosphate enzyme, which is required for the conversion of glycogen to glucose.
- Long-term SER stress, on the other hand, may contribute to the onset and progression of a variety of illnesses, including neurodegeneration, atherosclerosis, type 2 diabetes, liver disease, and even cancer.
Click Here for Complete Biology Notes
Important Differences between Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum and Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
What is PhD : Meaning, How to Do, Benefits, Full Details
Rough vs Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Citations
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/neuroscience/ribosome
- https://www.quora.com/How-are-the-golgi-apparatus-and-nucleus-related
- https://www.mpg.de/36350/bm10_Proteinfolding-basetext.pdf
- https://www.endocrineweb.com/endocrinology/overview-adrenal-glands
- https://vivadifferences.com/smooth-vs-rough-endoplasmic-reticulum/
- https://sciencemonk.com/endoplasmic-reticulum/
- https://quizlet.com/21343918/cell-organelles-functions-flash-cards/
- https://quizlet.com/164089069/ribosomes-flash-cards/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rough_endoplasmic_reticulum
- https://brainly.com/question/13390727
Related Posts
- Phylum Porifera: Classification, Characteristics, Examples
- Dissecting Microscope (Stereo Microscope) Definition, Principle, Uses, Parts
- Epithelial Tissue Vs Connective Tissue: Definition, 16+ Differences, Examples
- 29+ Differences Between Arteries and Veins
- 31+ Differences Between DNA and RNA (DNA vs RNA)
- Eukaryotic Cells: Definition, Parts, Structure, Examples
- Centrifugal Force: Definition, Principle, Formula, Examples
- Asexual Vs Sexual Reproduction: Overview, 18+ Differences, Examples
- Glandular Epithelium: Location, Structure, Functions, Examples
- 25+ Differences between Invertebrates and Vertebrates
- Lineweaver–Burk Plot
- Cilia and Flagella: Definition, Structure, Functions and Diagram
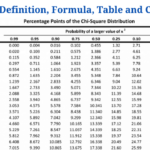
- P-value: Definition, Formula, Table and Calculation
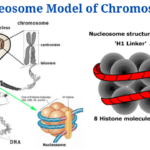
- Nucleosome Model of Chromosome
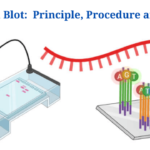
- Northern Blot: Overview, Principle, Procedure and Results