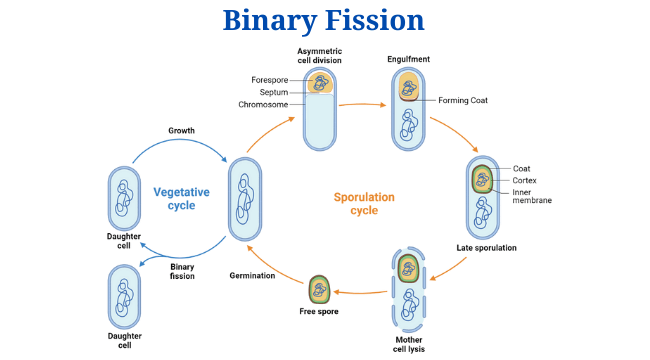
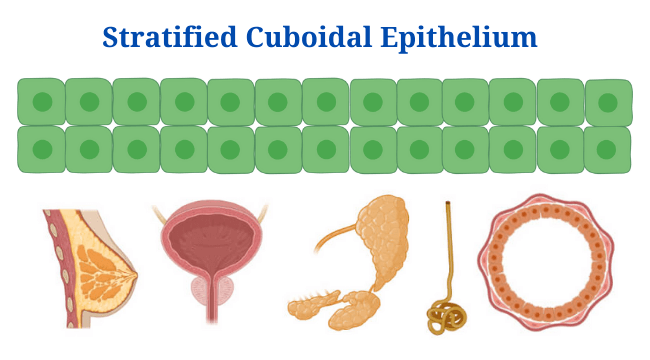
Morphology of Bacteria: Arrangement, Shapes, Sizes, Diagram, Examples
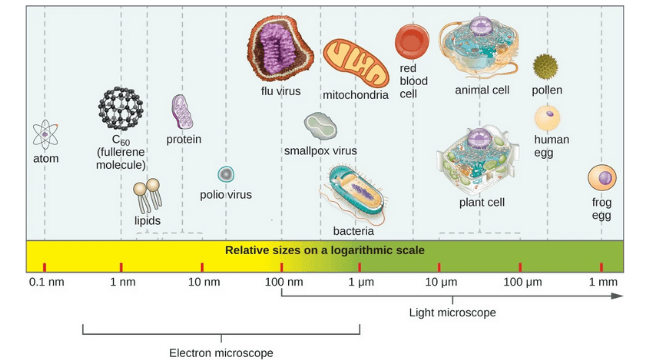
Morphology of Bacteria Bacteria are a sort of unicellular prokaryotic biological cell. Since they lack a membrane-bound nucleus, they are simpler than other forms of living creatures. Even though simply a few can be seen with the human eye and the rest are minuscule, they come in a variety of shapes, sizes, and architectures. Bacterial … Read more