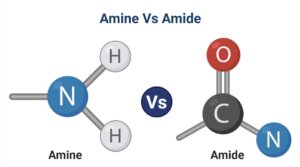
Definition of Amine
Amines are organic compounds formed when one or more hydrogen atoms linked to the nitrogen atom are replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group.
- Amines are essential organic molecules because they are the building blocks of life systems, forming amino acids and proteins.
- Inorganic ammonia derivatives are also known as amines. An amino group is the name given to the substituent –NH2 present in a variety of chemical molecules.
- Amines are classified as arylamines or alkylamines based on the presence of alkyl or aryl groups linked to the amino group.
- Aside from that, amines are further categorised into three types: primary amines, secondary amines, and tertiary amines.
- Primary amines are amines in which an alkyl or aryl group replaces one of the three hydrogen atoms linked to the nitrogen atom.
- Secondary amines are amines in which an alkyl or aryl group replaces two of the three hydrogen atoms linked to the nitrogen atom.
- Tertiary amines are amines in which an alkyl or aryl group replaces all three hydrogen atoms linked to the nitrogen atom.
- Amines can be named using either the prefix ‘amino’ or the suffix ‘amine.‘
- Intermolecular and intramolecular hydrogen bonding influence the chemical and physical properties of amines.
- Because of the existence of a lone pair of electrons in the nitrogen atom, amines have basic characteristics.
- Different amines, such as aniline and ethanolamines, are used in the production of rubber, colours, and pharmaceutical items.
- These amines can be synthesised through chemical reduction of other kinds of organic nitrogen molecules or through processes involving ammonia and other organic chemicals.
Definition of Amide
Amides are ammonia derivatives in that the carbon atom of a carbonyl group replaces one or more hydrogen atoms linked to the nitrogen atom.
- When present in the primary chain of proteins, the amide group indicates a peptide bond, and when present in the side chain, it represents an isopeptide bond.
- Amides, or the amide group, are a carboxylic acid derivative in which the hydroxyl group is substituted with an amine group. These are known as carboxamides.
- Amides, like amines, are classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary amides depending on whether one, two, or three hydrogen atoms linked to nitrogen in the amine group are replaced.
- Amides are called by appending the suffix ‘amide’ to the name of the parent acid.
- Because of the presence of a carbonyl group, which lessens the basicity of the –NH2 group, the amides are neutral to slightly acidic.
- Except for formaldehyde, which occurs in liquid form, amides generated from ammonia are usually solids. Amides with five or fewer carbon atoms are water soluble, but the others are not.
- Amides have a higher boiling point and work well as solvents for organic and inorganic molecules.
- Polyamides are amides that have been joined together to form bigger molecules and are abundant in the protein systems of living creatures.
- One of the most essential properties of amides is their ability to hydrolyze to generate acids and amines. A strong acid or basic can catalyse the process, which is extremely sluggish.
Key Differences between Amine and Amide
(Amine Vs Amide)
Amines examples
Dopamine
- Dopamine is an organic molecule belonging to the catecholamine as well as phenethylamine families that is crucial in the neurological system of living organisms.
- A catechol structure with an amino group connected via an ethyl chain makes up a dopamine molecule.
- Dopamine, also known as substituted phenethylamine, is the most basic catecholamine.
- Dopamine is a water-soluble organic base that is relatively stable compared to other amines.
- Dopamine is produced by a variety of cell types, including neurons as well as medulla cells in the adrenal glands.
- Dopamine is necessary for signal transmission since it binds to as well as activates cell surface receptors. Specific receptors on these molecules are involved in the receiving as well as transmission of brain impulses.
Amides examples
Acetamide
- Acetamide, also known as ethanamide, is the most basic amide formed from acetic acid.
- Acetamide is formed by the formal condensation of acetic acid as well as ammonia as well as has the chemical formula CH3CONH2. It’s frequently used as a bridge between acetone as well as urea.
- Acetamide is primarily employed as a plasticizer as well as a solvent. From acute to chronic exposure, it might cause moderate skin irritation.
- Acetamide is also used as a stabilizer as well as fire suppressor as well as is required for the synthesis of methylamine.
Amine Vs Amide Citations
- https://www.coursehero.com/file/9806557/chapter16-Amines-and-Amides-1/
- https://www.coursehero.com/file/67658923/exam-4pdf/
- https://www.chegg.com/homework-help/questions-and-answers/6-methylamine-ch3nh2-important-industrial-chemical-production-various-pharmaceuticals-pest-q45335022
- https://www.britannica.com/science/amine
- https://www.britannica.com/science/amide
- https://www.askdifference.com/amide-vs-amine/
- https://vivadifferences.com/difference-between-amine-and-amide/
- https://guides.hostos.cuny.edu/che120/chapter5
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carboxamide
- https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amine
- https://deemagclinic.com/2017/04/14/3310/
- https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Organic_Chemistry/Supplemental_Modules_(Organic_Chemistry)/Carboxylic_Acids/Properties_of_Carboxylic_Acids/Carboxyl_Derivatives
- https://askinglot.com/what-is-the-structure-of-acetamide
- https://answers.yahoo.com/question/index?qid=20100710093318AAcXtlf
- https://answers.yahoo.com/question/index?qid=20090504063210AAhAr2n
- https://www.bioexplorer.net/building-blocks-of-proteins.html/
- https://quizlet.com/204220829/chem-test-4-flash-cards/
- https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/acetamide
Related Posts
- Dissecting Microscope (Stereo Microscope) Definition, Principle, Uses, Parts
- Saturated vs Unsaturated Hydrocarbons: Definition, Differences, Examples
- Ethanol Vs Methanol: Definition and 10+ Differences
- Hydrogen Bond: Properties, Definition, Types, Examples
- Nitrate Vs Nitrite: Definition, Differences, Examples
- Aromatic Compounds vs Aliphatic Compounds: Definition, Differences, Examples
- Compound Vs Mixture: Definition, Differences, Examples
- Elements Vs Compounds: Definition, Differences, Examples
- Molecules Vs Compounds: Definition, Differences, Examples
- Hard water Vs Soft water: Definition, Differences, Examples
- Glucose Vs Sucrose: Definition and Key Differences
- 13+ Difference Between Atom and Molecule with Examples
- How to Balance Chemical Equation: Methods, Steps, Examples
- Ionic Bond: Definition, Properties, Examples
- Amylase Vs Amylose: Definition, Differences, Example